比如relative和absolute定位
fixed定位与relative的关系
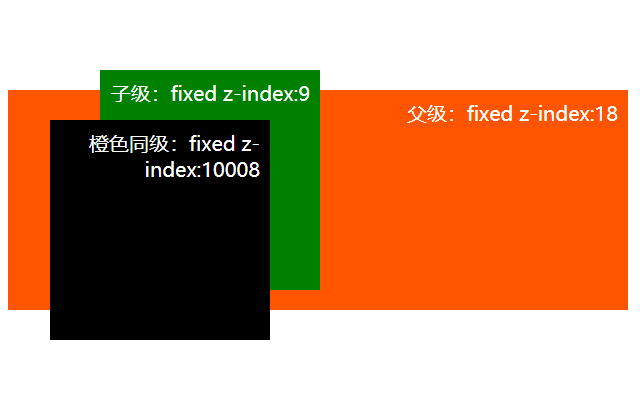
下面这个小demo演示一下fixed与父级子级同级的效果展示
这三个div都是【fixed】属性,但你会发现父级的zindex这时压根没盖过子级的z-index
同级的情况下是会被遮罩住的。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>fixed</title>
<style>
body {
min-height: 1500px;
font-size: 20px;
}
.rel {
position: fixed;
top: 120px;
background: #f50;
width: 600px;
height: 200px;
z-index: 10008;
text-align: right;
color: #fff;
padding: 10px;
}
.fixed {
position: fixed;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: green;
z-index: 9;
color: #fff;
padding: 10px;
}
.other {
position: fixed;
top: 150px;
left: 50px;
background: #000;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
z-index: 10008;
text-align: right;
color: #fff;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="rel">
父级:fixed z-index:18
<div class="fixed">子级:fixed z-index:9</div>
</div>
<div class="other">橙色同级:fixed z-index:10008</div>
</body>
</html>
本文著作权归作者 [ admin ] 享有,未经作者书面授权,禁止转载,封面图片来源于 [ 互联网 ] ,本文仅供个人学习、研究和欣赏使用。如有异议,请联系博主及时处理。